前言
开发中很多情况下需要进行对数据的排序,然而经常用到Map来储存值进行排序。下面给大家详细介绍一下map的key 与 value的值升序降序排序
下面Collections.reverse(list);的作用主要将升序排好的进行降序具体详细看下面
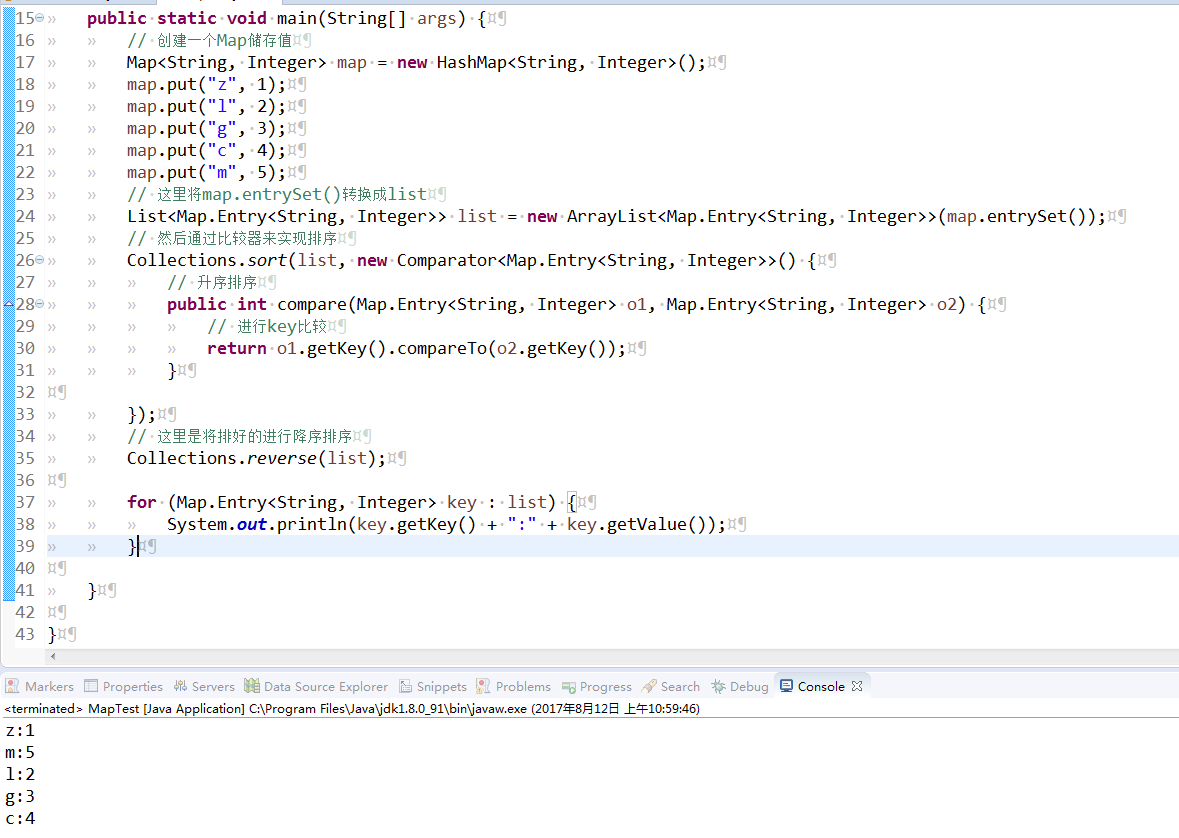
Map中key的升序排序
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;public class MapTest {
/**
* 升序排序
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Map储存值
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put(“z”, 1);
map.put(“l”, 2);
map.put(“g”, 3);
map.put(“c”, 4);
map.put(“m”, 5);
// 这里将map.entrySet()转换成list
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
// 然后通过比较器来实现排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
// 升序排序
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
//进行key比较
return o1.getKey().compareTo(o2.getKey());
}});
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> key : list) {
System.out.println(key.getKey() + “:” + key.getValue());
}}
}
Map中key的降序排序
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;public class MapTest {
/**
* 降序排序
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Map储存值
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put(“z”, 1);
map.put(“l”, 2);
map.put(“g”, 3);
map.put(“c”, 4);
map.put(“m”, 5);
// 这里将map.entrySet()转换成list
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
// 然后通过比较器来实现排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
// 降序排序
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
// 进行key比较
return o1.getKey().compareTo(o2.getKey());
}});
// 这里是将排好的进行降序排序
Collections.reverse(list);for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> key : list) {
System.out.println(key.getKey() + “:” + key.getValue());
}}
}
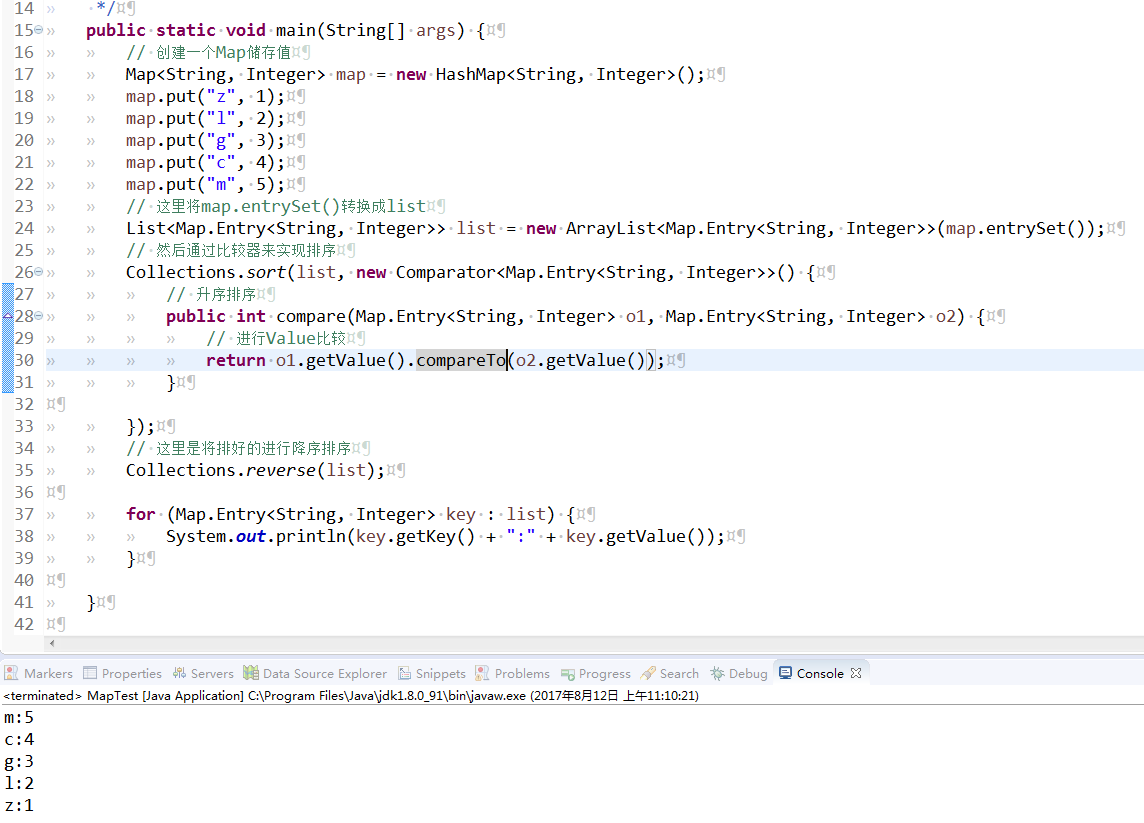
Map中Value的升序排序
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;public class MapTest {
/**
* 升序排序
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Map储存值
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put(“z”, 1);
map.put(“l”, 2);
map.put(“g”, 3);
map.put(“c”, 4);
map.put(“m”, 5);
// 这里将map.entrySet()转换成list
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
// 然后通过比较器来实现排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
// 升序排序
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
// 进行Value比较
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}});
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> key : list) {
System.out.println(key.getKey() + “:” + key.getValue());
}}
}
Map中Value的降序排序
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;public class MapTest {
/**
* 降序排序
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个Map储存值
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put(“z”, 1);
map.put(“l”, 2);
map.put(“g”, 3);
map.put(“c”, 4);
map.put(“m”, 5);
// 这里将map.entrySet()转换成list
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
// 然后通过比较器来实现排序
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
// 升序排序
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
// 进行Value比较
return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue());
}});
// 这里是将排好的进行降序排序
Collections.reverse(list);for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> key : list) {
System.out.println(key.getKey() + “:” + key.getValue());
}}
}



没学Java看不懂
好久没来看你邻居我了,望回访,哈哈
中秋快乐!
代码格式有点差。